Introduction to Network Security
What is Network Security? In today’s digitally connected world, the importance of safeguarding our networks cannot be overstated. Network security is the practice of protecting the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data and resources as they are transmitted across or accessible from a network. Whether you are an individual browsing the internet or a multinational corporation conducting online transactions, network security is essential in preventing unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
Why is Network Security Important?
The significance of network security stems from the ever-growing number of cyber threats that can target individuals, organizations, and governments. A successful cyberattack can lead to severe consequences, including financial loss, damage to reputation, legal liabilities, and even national security risks. With the increasing reliance on digital infrastructure, ensuring robust network security is more crucial than ever.
Key Concepts in Network Security
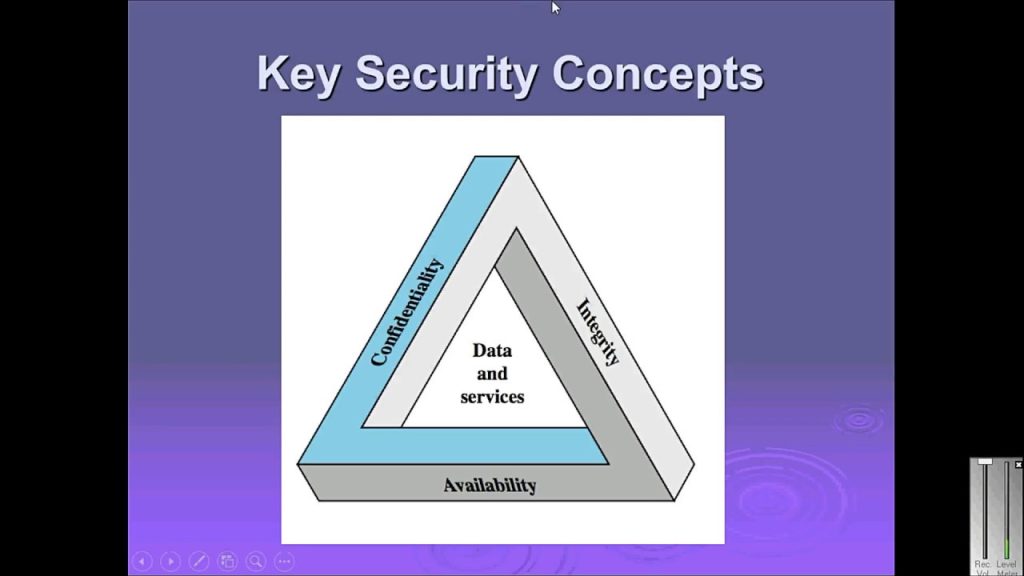
1. Confidentiality
Confidentiality involves ensuring that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals. This is often achieved through encryption and access control measures. The goal is to prevent unauthorized users from accessing private data, whether it is in transit or stored on servers.
2. Integrity
Integrity refers to maintaining the accuracy and consistency of data throughout its lifecycle. It ensures that data is not altered or tampered with by unauthorized individuals. Techniques like hashing and digital signatures are commonly used to verify the integrity of data.
3. Availability
Availability ensures that network services and data are accessible to authorized users whenever they are needed. This involves implementing measures to protect against Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks and other threats that could disrupt service.
Types of Network Security Threats
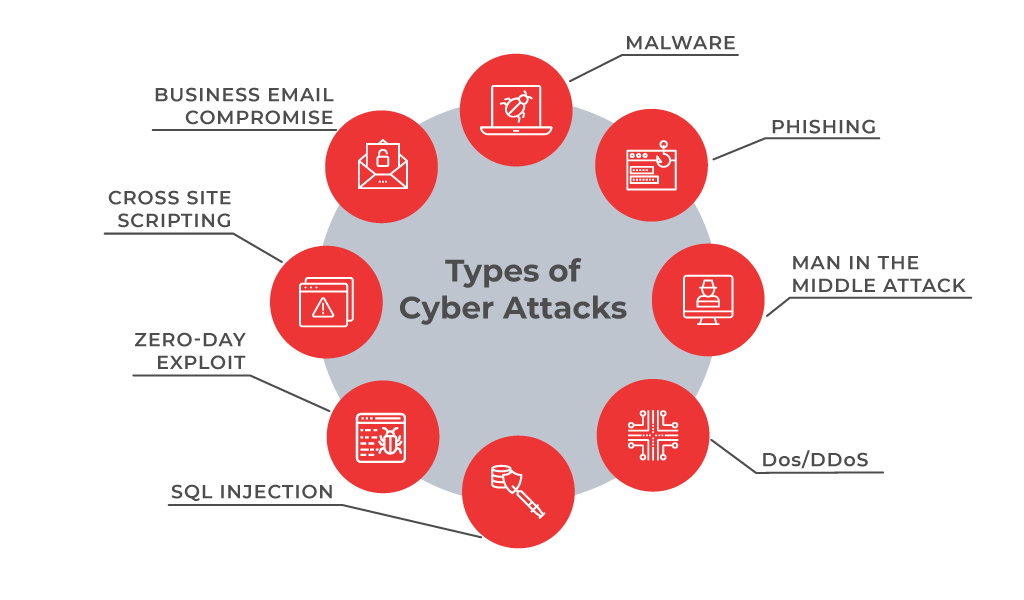
1. Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, is designed to damage or disrupt computer systems. This includes viruses, worms, trojans, and ransomware. Malware can steal sensitive data, corrupt files, or take control of systems, leading to significant security breaches.
2. Phishing
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack where attackers trick individuals into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials or credit card numbers. This is typically done through fraudulent emails, websites, or messages that appear to be from legitimate sources.
3. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
In a MitM attack, an attacker intercepts and potentially alters the communication between two parties without their knowledge. This can lead to the theft of sensitive information or the manipulation of data being transmitted.
4. Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
DoS attacks aim to make a network service unavailable by overwhelming it with a flood of illegitimate requests. This can cripple websites, online services, and even critical infrastructure if not properly mitigated.
5. SQL Injection
SQL injection is a technique used by attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in web applications by injecting malicious SQL code into a query. This can result in unauthorized access to databases, allowing attackers to retrieve, alter, or delete sensitive data.
Network Security Technologies and Tools
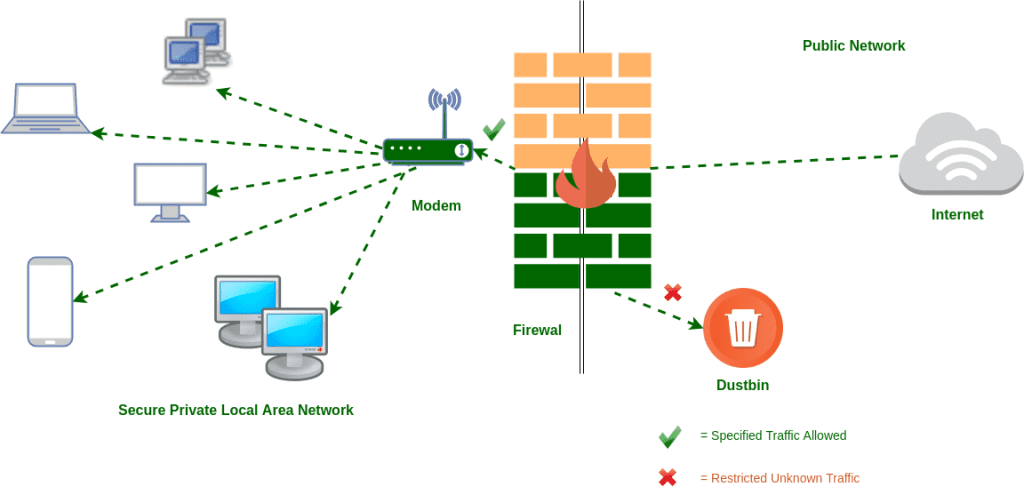
1. Firewalls
Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks. They filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules, helping to prevent unauthorized access and attacks.
2. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
IDS monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and potential threats. They can detect anomalies, such as unusual patterns of behavior or known attack signatures, and alert administrators to take action.
3. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
VPNs create a secure, encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the internet. This allows users to access resources on a private network remotely while protecting the data in transit from eavesdropping.
4. Encryption
Encryption converts data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. It is used to protect sensitive information both at rest (stored data) and in transit (data being transmitted over networks).
5. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a system. This might include something the user knows (password), something they have (security token), or something they are (biometric verification).
Best Practices for Network Security
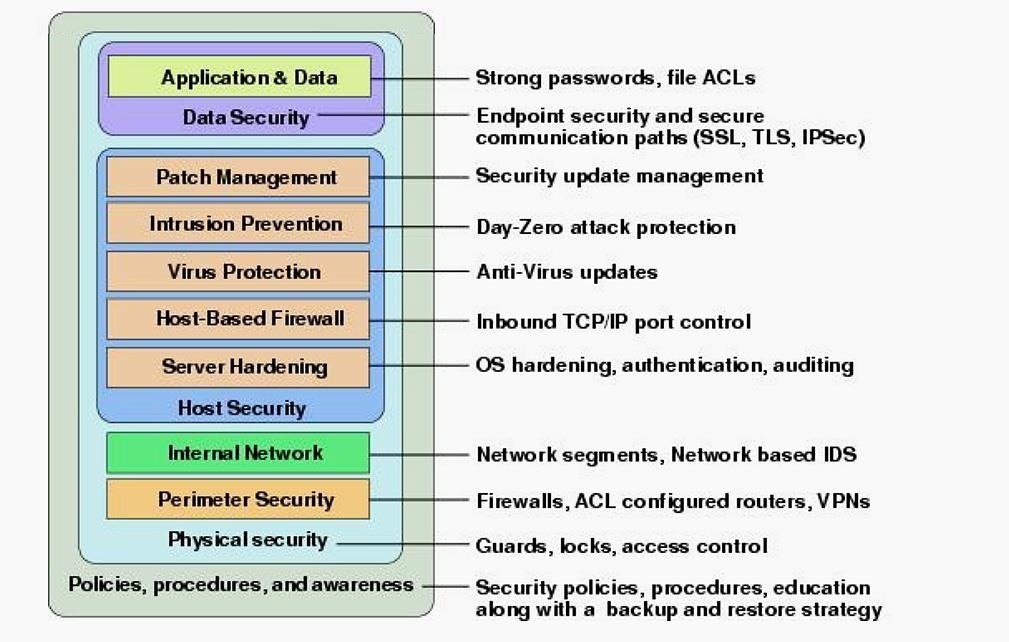
1. Regular Updates and Patch Management
Keeping software and systems up to date is crucial in mitigating vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Regular patch management helps close security gaps and protect against the latest threats.
2. Strong Password Policies
Enforcing strong, unique passwords for all accounts reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Password policies should include guidelines for complexity, expiration, and avoidance of reuse.
3. Employee Training
Human error is a common factor in security breaches. Regular training ensures that employees are aware of security best practices, recognize phishing attempts, and understand the importance of safeguarding sensitive information.
4. Network Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of network traffic helps in the early detection of suspicious activities and potential threats. Network monitoring tools can alert administrators to abnormal behavior and allow for prompt response.
5. Incident Response Plan
Having a well-defined incident response plan ensures that an organization is prepared to react swiftly and effectively in the event of a security breach. This plan should include steps for containment, eradication, recovery, and communication.
The Future of Network Security
As technology evolves, so do the threats to network security. The future will likely see the rise of more sophisticated attacks, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence and quantum computing. To counter these threats, security measures will need to become more adaptive, leveraging AI and machine learning to predict and respond to potential attacks in real-time. Additionally, the growing adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) devices will necessitate new security protocols and standards to protect interconnected systems.
Conclusion
Network security is a critical aspect of the digital age, essential for protecting data, maintaining privacy, and ensuring the smooth operation of businesses and governments. By understanding the key concepts, threats, and best practices in network security, individuals and organizations can better defend against cyberattacks and secure their networks in an ever-changing threat landscape.
